Research
Research interests
- Spatial Sensing and Modeling; Real-time Automated Construction Operation Analysis; Construction Resource Field Mobility and Status Monitoring
- Construction Simulation; Site Layout and Internal Traffic Control Plan
- Construction Informatics; Computational Data Analysis, Statistics and Algorithms; Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
- Data Visualization and Virtual Reality; Building Information Modeling (BIM)
- Sensing and Surveying Technologies in Construction: Global Positioning System (GPS), Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Ultra Wideband (UWB), Robotic Total Station (RTS), Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), Laser Scanner
- Construction Management; Construction Education and Training; Construction Safety and Health; Project Planning and Progress Monitoring
Ongoing Research
Past Research Experience
-
Construction resources (workers, equipment and material) continuously interact with each other to accomplish their regular tasks. Most part of this interaction is spatio-temporal and happen towards completing the physical form of an infrastructure. The resources are tracked using location tracking technologies in this research.
A data management tool was created to accumulate hard data (real-time location of resources, site geometry, photographs and information about equipment) and soft data (site notes, manually designated zones and management plans).
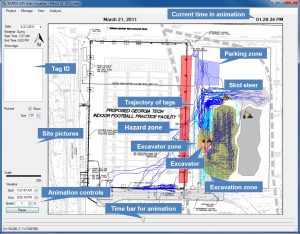
Results include (i) automatic analysis of cyclic activities, (ii) proximity analysis among different pieces of equipment and (iii) zone and speed analysis to assess safety and productivity of the construction site.
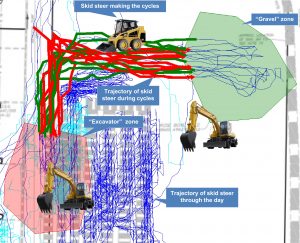
Resulting publication(s);
- Pradhananga, N. and Teizer, J. (2013) “Automatic Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Construction Equipment Operations using GPS Data”, Automation in Construction, 29, 107-122.
- Ergun, H. and Pradhananga, N. (2015) “Real-time Location Data for Automated Learning Curve Analysis of Linear Repetitive Construction Activities”, 2015 ASCE International Workshop on Computing in Civil Engineering, Austin, TX, June 12-23, 2015.
- Pradhananga, N. and Teizer, J. (2012) “GPS-Based Framework towards more Realistic and Real-time Construction Equipment Operation Simulation”, Proceedings of the 2012 Winter Simulation Conference, Berlin, Gemany, December 9-12, 2012.
- Pradhananga, N. and Teizer, J. (2012) “Spatio-Temporal Safety Analysis of Construction Site Operations using GPS Data”, Construction Research Congress, West Lafayette, Indiana, May 21-23, 2012.
-
Human-equipment interactions on a construction site are inevitable. Yet, most of the accidents occur during such interactions. This research studies the factors that expose ground worker to potential hazards during such interactions.
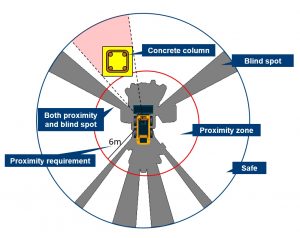
Factors like blind spots, proximity, velocity of travel, angle of approach and occlusion on the site are considered to devise a model to automatically identify potential hazards for ground workers on a site.
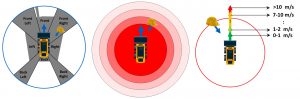
Each instance (depends upon the frequency of data collection) is analyzed based on pre-defined hazard model. This model is created from historical statistics of accidents, mathematical and physical model of moving equipment and empirical values based on experience.
By classifying and analyzing each and every instances, heat maps can be generated for the site that can visually guide the safety manager to potentially unsafe parts of the site and also helps him/her identify workers or operations requiring attention in terms of safety.

Resulting publication(s):
- Golovina, O., Teizer, J., and Pradhananga, N. (2016) “Heat map generation for predictive safety planning: Preventing struck-by and near miss interactions between workers-on-foot and construction equipment”, Automation in Construction.
- Shen, X., Marks, E., Pradhananga, N. and Cheng, T. (2016) “Hazardous Proximity Zone Design for Heavy Construction Excavation Equipment”, Journal of Construction Engineering and Management.
- Teizer, J., Golovina, O., Wang, D. and Pradhananga, N. (2015) “Automated Collection, Identi cation, Localization, and Analysis of Worker-Related Proximity Hazard Events in Heavy Construction Equipment Operation”, The 32th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction and Mining, Oulu, Finland, June 15-18, 2015.
- Awolusi, I. G., Marks, E., Pradhananga, N. and Cheng, T. (2015) “Hazardous Proximity Zone Design for Heavy Construction Equipment”, The CSCE International Construction Specialty Conference, Vancouver, Canada, June 7-10, 2015.
- Cheng, T., Pradhananga, N., and Teizer, J. (2013) “Automated Evaluation of Proximity Hazards Caused by Workers Interacting with Equipment”, The 30th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction and Mining, Montreal, Canada, August 11-15, 2013.
-
From an owner’s perspective, operation and maintenance phase of a project is more important in terms of cost and time. Building Information Models (BIM) are used extensively in pre-construction and construction phases of projects but the information-rich models find no use in the operation phase.
On the other hand, facility managers suffer in terms of productivity and quality because of unavailability of an up-to-date digital copy of a facility.
To solve the above-mentioned problems, this research explores the use of BIM for facility management.

This research uses passive RFID tags to enable indoor localization in large facilities and pin-point ones location based on the tags and location information in BIM. A part of this research deals with developing a visually guiding system to navigate inside a large facility based on the RFID tags and BIM.
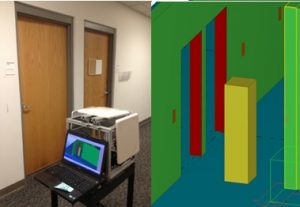
The research assumes ubiquitous deployment of RFID tags. The same RFID tags can be used in procurement, construction as well as maintenance of the component of a facility.

The research also equips the navigation system with a database which can store all the necessary information required for facility managers. The entire maintenance system is digitized and automated to save on money and time and increase the overall service life of the facility.
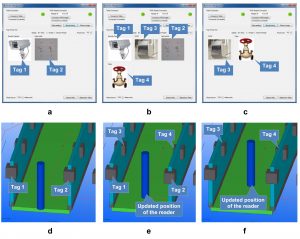
Resulting publication(s):
- Costin, A., Pradhananga, N. and Teizer, J. (2014) “Passive RFID and BIM for Real-Time Visualization and Location Tracking”, Construction Research Congress, Atlanta, Georgia, May 19-21, 2014.
- Costin, A., Pradhananga, N., Teizer, J. and Marks, E. (2012) “Realtime Resource Location Tracking in Building Information Models”, The 9th International Conference on Cooperative Design Visualization and Engineering, Osaka, Japan, September 2-5, 2012.
- Costin, A., Pradhananga, N. and Teizer, J. (2012) “Integration of Passive RFID Location Tracking in Building Information Models”, International Workshop: Intelligent Computing in Engineering, Herrsching (Munich), Germany, July 4-6, 2012.
-
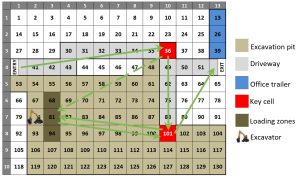
Space is a major constrain in urban construction sites. Complex system simulation consisting of cells consider space (cells) as the basis of simulation and allow us to understand how spatial interaction of different resources will affect the efficiency of a construction site.
The case below demonstrates an earthmoving operation. The site geometry was recorded through multiple laser scans and the movement of excavator, dozer, loader and trucks were recorded by GPS tags attached to them.
Cell-based simulation engine was coded from the scratch and real-time data from the field was used to validate the simulation engine and the simulation model.

Construction sites layout plan was converted to a system of cells in this research and the resources that were occupying space (cells) on the sites were controlled by their spatial interactions. These pre-defined interactions governed their movement and occupancy of cells. This process was repeated for different resource combination to optimize resources, minimize close resource interactions (for safety) and maximize productivity.
Resulting publication(s):
- Pradhananga, N., and Teizer, J. (2015) “Cell-based construction site simulation model for earthmoving operations using real-time equipment location data”, Visualization in Engineering, 3(1), 1-16.
- Pradhananga, N. and Teizer, J. (2014) “Congestion Analysis for Construction Site Layout Planning using Real-time Data and Cell-based Simulation Model”, 2014 International Society for Computing in Civil and Building Engineering (ISCCBE) Conference, Orlando, FL, June 23-25, 2014.
- Pradhananga, N. and Teizer, J. (2014) “Development of a Cell-based Simulation Model for Earthmoving Operation using Real-time Location Data”, Construction Research Congress, Atlanta, Georgia, May 19-21, 2014.
-
Vertical construction projects face unique challenges. Resource mobility can sometime be the bottleneck for efficient project execution.
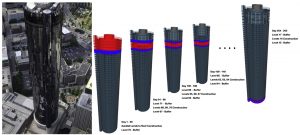
Resources (buck hoists, workers, material) were tracked with passive RFID technology to study the feasibility of the technology for resource field mobility and status monitoring and to learn about the challenges in vertical renovation projects. Image below shows the placement of tags for the experiment.

The research discovered advantages and challenges in deploying RFID for resource tracking. A cost-benefit analysis revealed that implementation of the technology can potentially also offer economic advantage to the project.
Resulting publication(s):
- Costin, A., Pradhananga, N. and Teizer, J. (2012) “Leveraging Passive RFID Technology for Construction Resource Field Mobility and Status Monitoring in a High-Rise Renovation Project”, Automation in Construction, 24, 1-15.
-
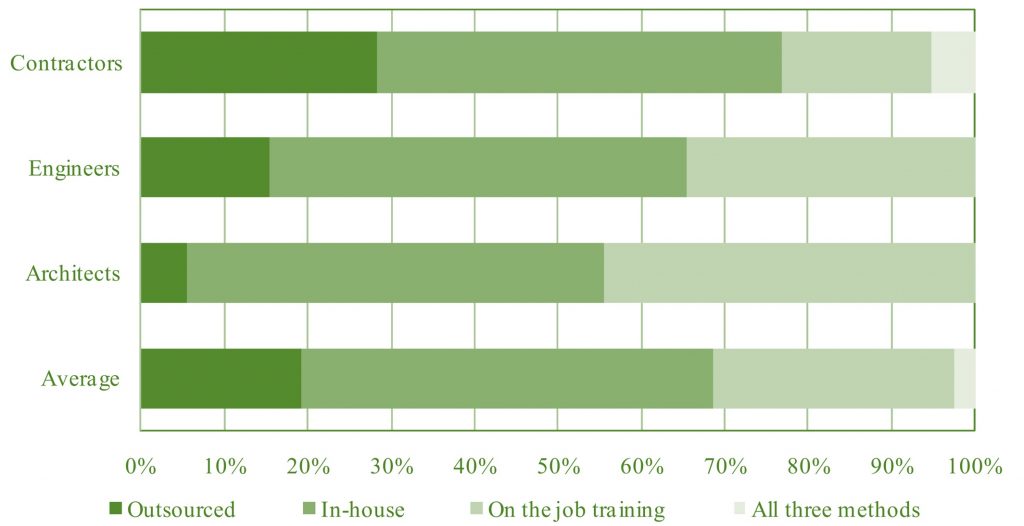
In conjunction to developing the technologies, it is also crucial for researchers to keep track of technological status and readiness of the industry to adapt to the emerging technologies. This research studied the status of information technology use in A/E/C industries in Southern Nevada.
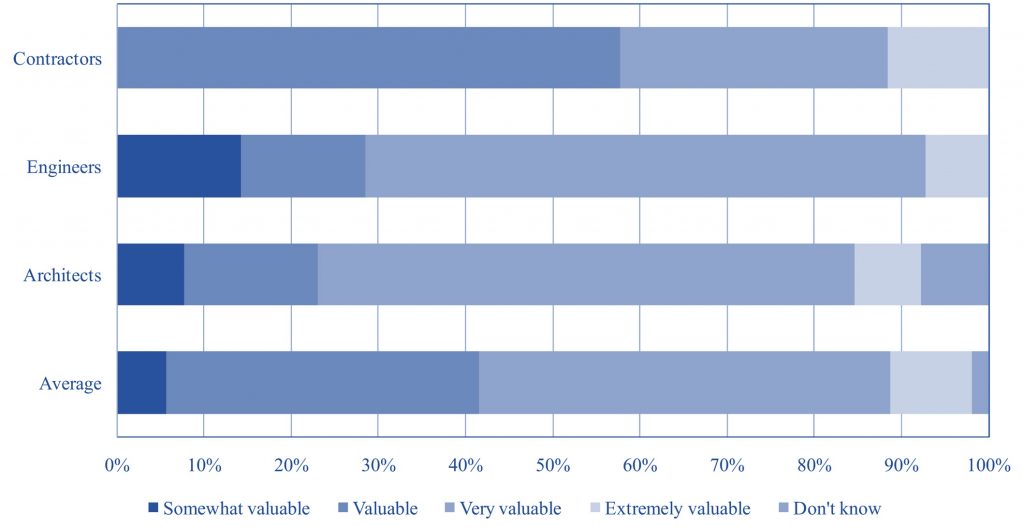
The participants were small to big companies and were surveyed on their perception of information technology, their level of use, desire to learn and wishlist.
Resulting publication(s):
- Shrestha, P. P., Shields, D.R., Oparagua, D., and Pradhananga, N. (2011) “Comparative Study of Information Technology Use by Architects, Engineers and Contractors”, Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 5 (5), 375-388.
- Shrestha, P. P., Shields, D. R., and Pradhananga, N. (2010) “Information Technology in Southern Nevada A/E/C Industries”, Associated Schools of Construction 46th Annual International Conference, Boston, Massachusetts, April 7-10, 2010.
-
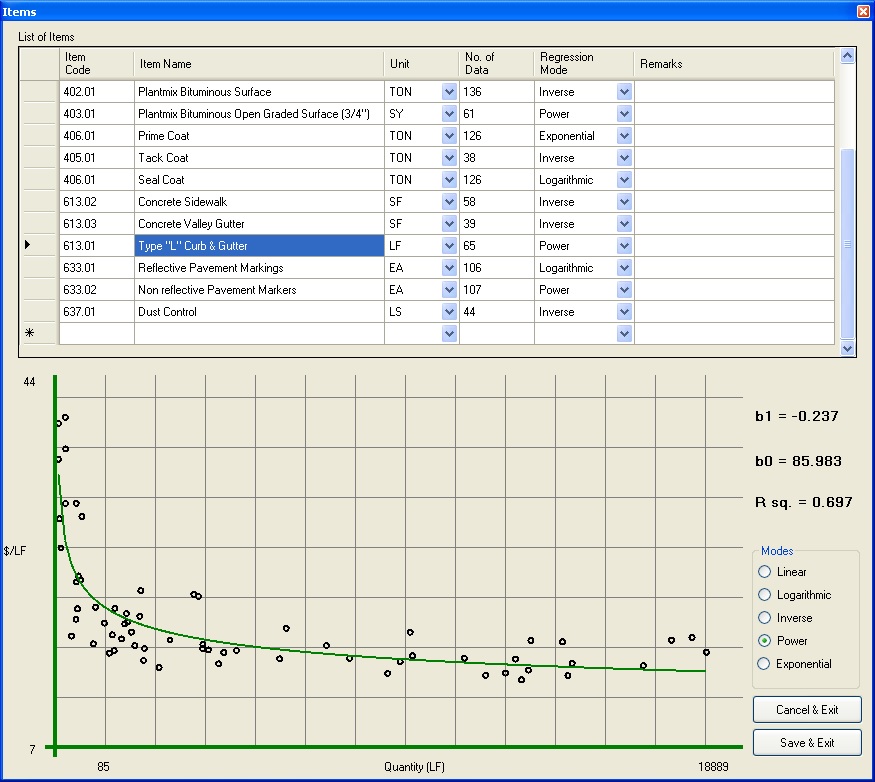
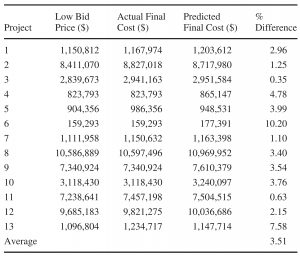
Irrespective of estimate of an engineer, the final project cost to the owner will be the final completion cost of the project. In order to assist public agencies better predict the final completion costs of street construction projects, an analysis was done based on historical bid data for similar projects.
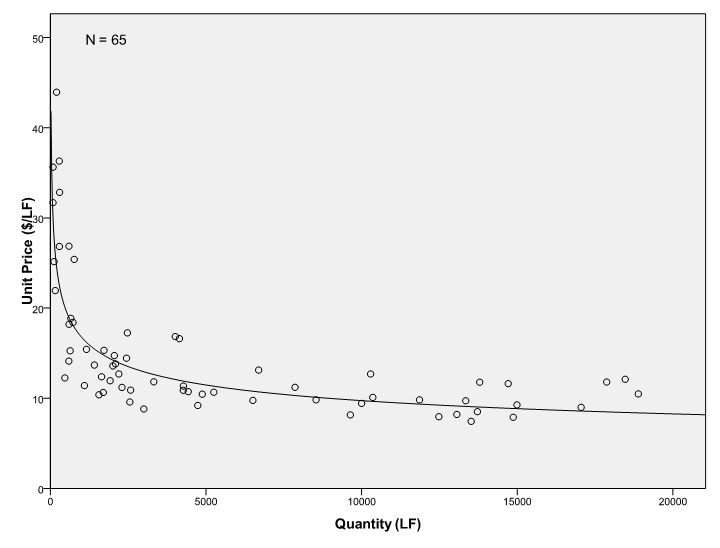
Based on historical bid data from unit price items, a dynamic method of predicting final construction cost was devised. A graphical user interface was developed to incorporate the findings of the research. Data from Clark County, NV was used for the research.
Resulting publication(s):
- Shrestha, P.P., Pradhananga, N. and Mani, N. (2014) “Correlating Quantity and Bid Cost of Unit Price Items of Public Road Projects”, KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 1-9.
-
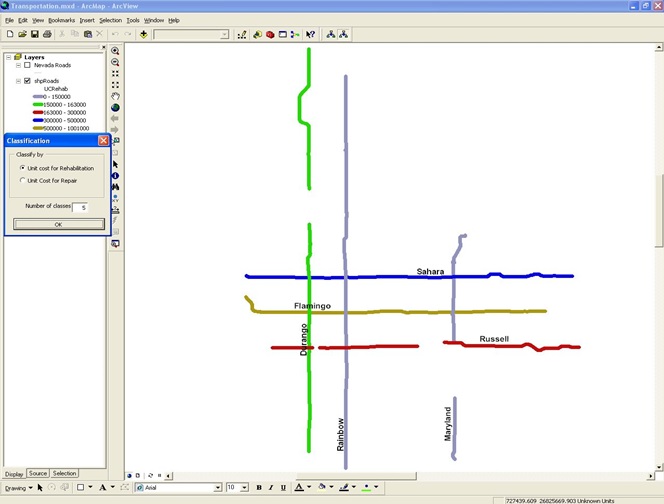
A system was developed to help agencies prioritize road maintenance schedule based on the condition of the pavement, budget available and planning years.
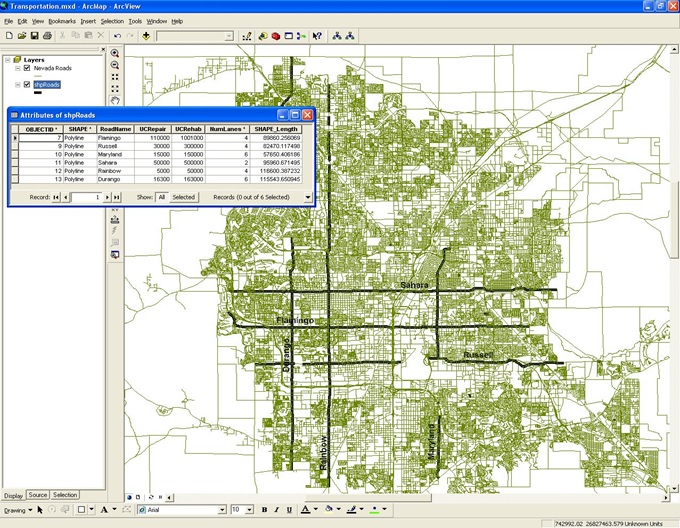
An ArcGIS-based UI was created that could visually present the results.
Resulting publication(s):
- Shrestha, P. P. and Pradhananga, N. (2009) “GIS-Based Road Maintenance Management”, International Workshop on Computing in Civil Engineering, Austin, Texas, June 24-27, 2009.
-
Understanding the patterns of bids in Design-Bid-Build projects can help in enhancing the bidding process and predicting the final construction cost of the projects before inviting the bids.
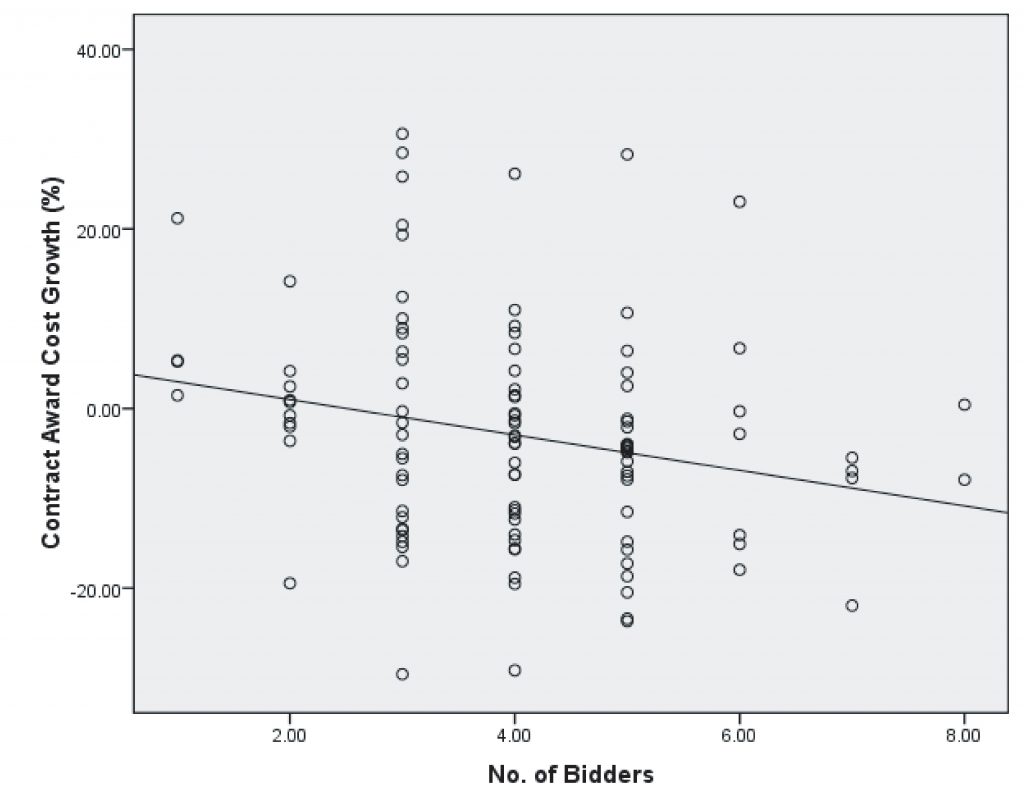
Data pertaining to street construction projects at Clark County, NV was used to analyze the cost growth and effect of number of bidders in street construction projects.
Resulting publication(s):
- Shrestha, P.P. and Pradhananga, N. (2010) \Correlating Bid Price with Number of Bidders and Final Construction Cost of Public Street Projects”, Transportation Research Record (Journal of Transportation Research Board), 2151-01, 3-10.
- Shrestha, P.P., Pradhananga, N. and Mani, N. (2012) “Impact of Quantity on Bid Cost of Unit Price Items in Design-Bid-Build Public Road Projects”, Transportation Research Board 91st Annual Meeting, Washington D.C., January 22-26, 2012.
- Shrestha, P.P. and Pradhananga, N. (2010) “Correlating Bid Price with Number of Bidders and Final Construction Cost of Public Street Projects”, Transportation Research Board 89th Annual Meeting, Washington D.C., January10-14, 2010.

